Coordenadas cartesianas. Diferenciales
De Laplace
Contenido |
1 Diferencial de camino
Aplicando la expresión general del diferencial de camino resulta
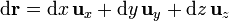
2 Diferenciales de superficie
Dependiendo de la coordenada que consideremos constante, tenemos tres vectores diferenciales de superficie:
- Superficie x = cte
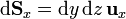
- Superficie y = cte
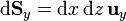
- Superficie z = cte
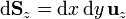
3 Diferencial de volumen
Combinando los tres diferenciales
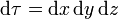
4 Enlaces
- Siguiente: Coordenadas cilíndricas. Diferenciales
- Anterior: Diferenciales





