Coordenadas esféricas. Diferenciales
De Laplace
(Diferencias entre revisiones)
(→Enlaces) |
(→Diferenciales de superficie) |
||
| (2 ediciones intermedias no se muestran.) | |||
| Línea 13: | Línea 13: | ||
*Superficie <math>\theta = \mathrm{cte}</math> (conos) | *Superficie <math>\theta = \mathrm{cte}</math> (conos) | ||
| - | <center><math>\mathrm{d}\mathbf{S}_\theta = r\,\mathrm{d}r\,\mathrm{d}\varphi\,\mathbf{u}_\theta</math></center> | + | <center><math>\mathrm{d}\mathbf{S}_\theta = r\,\mathrm{sen}\,\theta\,\mathrm{d}r\,\mathrm{d}\varphi\,\mathbf{u}_\theta</math></center> |
*Superficie <math>\varphi = \mathrm{cte}</math> (semiplanos verticales) | *Superficie <math>\varphi = \mathrm{cte}</math> (semiplanos verticales) | ||
| Línea 25: | Línea 25: | ||
==Enlaces== | ==Enlaces== | ||
| - | * '''Siguiente:''' [[ | + | * '''Siguiente:''' [[Cómo se hace una integral]] |
* '''Anterior:''' [[Coordenadas cilíndricas. Diferenciales]] | * '''Anterior:''' [[Coordenadas cilíndricas. Diferenciales]] | ||
| - | [[Categoría:Diferenciales]] | + | [[Categoría:Diferenciales|40]] |
| - | [[Categoría:Coordenadas esféricas]] | + | [[Categoría:Coordenadas esféricas|40]] |
última version al 17:58 13 abr 2010
Contenido |
1 Diferencial de camino
Aplicando la expresión general del diferencial de camino resulta
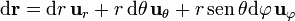
2 Diferenciales de superficie
Dependiendo de la coordenada que consideremos constante, tenemos tres vectores diferenciales de superficie:
- Superficie r = cte (superficies esféricas)
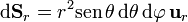
- Superficie θ = cte (conos)
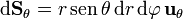
- Superficie
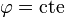 (semiplanos verticales)
(semiplanos verticales)
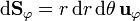
3 Diferencial de volumen
Combinando los tres diferenciales
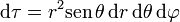
4 Enlaces
- Siguiente: Cómo se hace una integral
- Anterior: Coordenadas cilíndricas. Diferenciales





