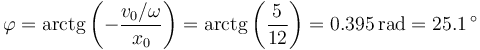Otro caso particular de MAS (GIOI)
De Laplace
Contenido |
1 Enunciado
Una partícula describe el movimiento armónico simple de ecuación horaria, en el SI,
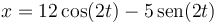
- ¿Cuanto vale la amplitud de las oscilaciones?
- ¿Cuánto vale la velocidad inicial?
- ¿Cuánto vale la fase inicial?
2 Amplitud
La solución general del m.a.s. puede escribirse en las formas
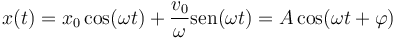
La relación entre ambas se obtiene desarollando el coseno de una suma e identificando coeficientes
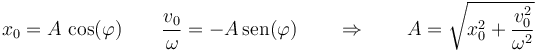
En nuestro caso
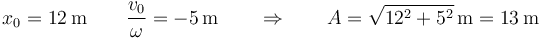
3 Velocidad inicial
Por las relaciones anteriores
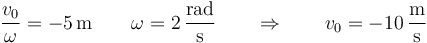
4 Fase inicial
De la misma manera