No Boletín - Area de un triángulo (Ex.Nov/16)
De Laplace
1 Enunciado
Sea 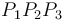 un triángulo de área
un triángulo de área 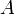 , y sea
, y sea  un punto coplanario con dicho triángulo e interior al mismo.
un punto coplanario con dicho triángulo e interior al mismo.
¿Cuál de las siguientes igualdades es falsa?
- (1)
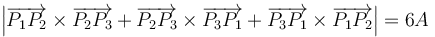
- (2)
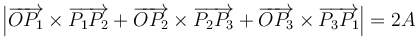
- (3)
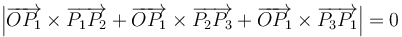
- (4)
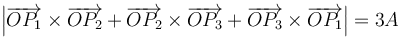
2 Solución
Empezamos examinando la igualdad (3), en la cual podemos sacar el vector 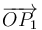 como factor común de la suma:
como factor común de la suma:
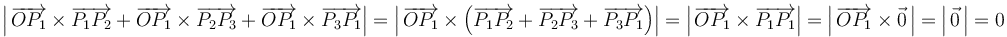
Por tanto, la igualdad (3) es correcta.
Un detalle importante que conviene observar en las igualdades (1), (2) y (4) es que todos los productos vectoriales que aparecen en ellas tienen la misma dirección (perpendicular al plano del triángulo) y el mismo sentido (saliente). Nótese que, sólo cuando se suman vectores que tienen la misma dirección y el mismo sentido, se puede igualar el módulo de la suma con la suma de los módulos. También vamos a utilizar la propiedad geométrica del producto vectorial que dice que "el módulo del producto vectorial de dos vectores es igual al doble del área del triángulo que tiene a ambos vectores como dos de sus lados".
Procedamos a examinar la igualdad (1):
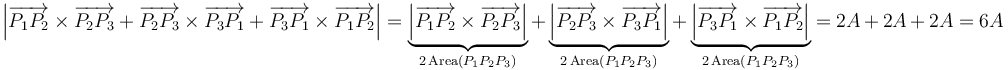
Por tanto, la igualdad (1) es correcta.
Procedamos a examinar la igualdad (2):
![\left|\overrightarrow{OP_1}\times\overrightarrow{P_1P_2}+\overrightarrow{OP_2}\times\overrightarrow{P_2P_3}+\overrightarrow{OP_3}\times\overrightarrow{P_3P_1}\right|=\underbrace{\underbrace{\underbrace{\left|\overrightarrow{OP_1}\times\overrightarrow{P_1P_2}\right|}_{2\,\mathrm{Area}(OP_1P_2)}+\underbrace{\left|\overrightarrow{OP_2}\times\overrightarrow{P_2P_3}\right|}_{2\,\mathrm{Area}(OP_2P_3)}+\underbrace{\left|\overrightarrow{OP_3}\times\overrightarrow{P_3P_1}\right|}_{2\,\mathrm{Area}(OP_3P_1)}}_{2\,[Area(OP_1P_2)\,+\,Area(OP_2P_3)\,+\,Area(OP_3P_1)]}}_{2\,\mathrm{Area}(P_1P_2P_3)}=2A](/wiki/images/math/6/5/3/653b7afce2c7da539c0abb7005092be2.png)
Por tanto, la igualdad (2) es correcta.
Procedamos a examinar la igualdad (4):
![\left|\overrightarrow{OP_1}\times\overrightarrow{OP_2}+\overrightarrow{OP_2}\times\overrightarrow{OP_3}+\overrightarrow{OP_3}\times\overrightarrow{OP_1}\right|=\underbrace{\underbrace{\underbrace{\left|\overrightarrow{OP_1}\times\overrightarrow{OP_2}\right|}_{2\,\mathrm{Area}(OP_1P_2)}+\underbrace{\left|\overrightarrow{OP_2}\times\overrightarrow{OP_3}\right|}_{2\,\mathrm{Area}(OP_2P_3)}+\underbrace{\left|\overrightarrow{OP_3}\times\overrightarrow{OP_1}\right|}_{2\,\mathrm{Area}(OP_3P_1)}}_{2\,[Area(OP_1P_2)\,+\,Area(OP_2P_3)\,+\,Area(OP_3P_1)]}}_{2\,\mathrm{Area}(P_1P_2P_3)}=2A\neq 3A](/wiki/images/math/c/f/7/cf794dc7c59a7a1ba3f28da755df98c3.png)
Por tanto, la afirmación (4) es la que es FALSA.






