Extract from "General Relativity"
De Laplace
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamical systems can be extraordinarily complicated; for example, a great number of processes can be going on in a star simultaneously. We want to try to explain the basic general ideas, restricting ourselves to the simplest systems.
During thermodynamical processes certain elements of matter, with their properties, remain conserved, for example, in non-relativistic thermodynamics molecules or atoms and their masses. In the course of transformations in star or during nuclear processes the baryons with their rest mass are conserved instead. We shall therefore relate all quantities to these baryons. If, for example, we choose a volume element of the system, then we shall take as four-velocity ui of this element the average baryon velocity. The flow (motion) of the system will therefore be characterized by a four-velocity field
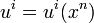 ,
,