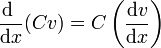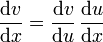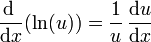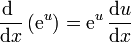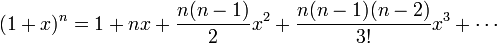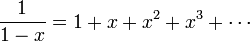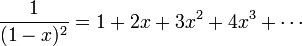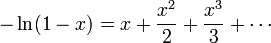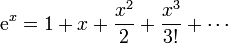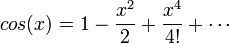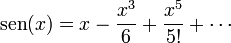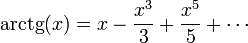Tabla de derivadas y primitivas
De Laplace
(Diferencias entre revisiones)
(→Series de Taylor) |
(→Tabla de primitivas) |
||
| (9 ediciones intermedias no se muestran.) | |||
| Línea 58: | Línea 58: | ||
| <math>\displaystyle -\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}</math> | | <math>\displaystyle -\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}</math> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | <math> | + | | <math>a^x\,</math> |
| - | | <math>\ln(a)\, | + | | <math>\ln(a)\,a^x</math> |
| <math>\mathrm{arctg}(x)\,</math> | | <math>\mathrm{arctg}(x)\,</math> | ||
| <math>\displaystyle\frac{1}{1+x^2}</math> | | <math>\displaystyle\frac{1}{1+x^2}</math> | ||
| Línea 72: | Línea 72: | ||
! <math>\int f\,\mathrm{d}x</math> | ! <math>\int f\,\mathrm{d}x</math> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | <math> | + | | <math>k\,</math> |
| - | | <math> | + | | <math>kx+C\,</math> |
| <math>\mathrm{sen}(x)\,</math> | | <math>\mathrm{sen}(x)\,</math> | ||
| - | | <math>-\cos(x)\,</math> | + | | <math>-\cos(x)+C\,</math> |
|- | |- | ||
| <math>x\,</math> | | <math>x\,</math> | ||
| - | | <math>\frac{x^2}{2}\,</math> | + | | <math>\frac{x^2}{2}+C\,</math> |
| <math>\cos(x)\,</math> | | <math>\cos(x)\,</math> | ||
| - | | <math>\mathrm{sen}(x)\,</math> | + | | <math>\mathrm{sen}(x)+C\,</math> |
|- | |- | ||
| <math>\frac{1}{x}\,</math> | | <math>\frac{1}{x}\,</math> | ||
| - | | <math>\ln|x|\,</math> | + | | <math>\ln|x|+C\,</math> |
| <math>\mathrm{tg}(x)\,</math> | | <math>\mathrm{tg}(x)\,</math> | ||
| - | | <math>-\ln | + | | <math>-\ln|\cos(x)|+C\,</math> |
|- | |- | ||
| <math>x^n \quad (n\neq -1)</math> | | <math>x^n \quad (n\neq -1)</math> | ||
| - | | <math>\frac{x^{n+1}}{n+1}</math> | + | | <math>\frac{x^{n+1}}{n+1}+C</math> |
| <math>\frac{1}{\mathrm{sen}(x)}</math> | | <math>\frac{1}{\mathrm{sen}(x)}</math> | ||
| - | | <math>\ln\left|\mathrm{tg}\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)\right|</math> | + | | <math>\ln\left|\mathrm{tg}\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)\right|+C</math> |
|- | |- | ||
| <math>\mathrm{e}^x\,</math> | | <math>\mathrm{e}^x\,</math> | ||
| - | | <math>\mathrm{e}^x\,</math> | + | | <math>\mathrm{e}^x+C\,</math> |
| <math>\frac{1}{1+x^2}</math> | | <math>\frac{1}{1+x^2}</math> | ||
| - | | <math>\mathrm{ | + | | <math>\mathrm{arctg}(x)+C\,</math> |
|- | |- | ||
| <math>\mathrm{e}^{\lambda x}\,</math> | | <math>\mathrm{e}^{\lambda x}\,</math> | ||
| - | | <math>\frac{1}{\lambda}\mathrm{e}^{\lambda x}\,</math> | + | | <math>\frac{1}{\lambda}\mathrm{e}^{\lambda x}+C\,</math> |
| <math>\displaystyle\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}</math> | | <math>\displaystyle\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}</math> | ||
| - | | <math>\mathrm{arcsen}(x)\,</math> | + | | <math>\mathrm{arcsen}(x)+C\,</math> |
|} | |} | ||
| - | Más | + | Más primitivas en la [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lists_of_integrals Wikipedia] |
==Series de Taylor== | ==Series de Taylor== | ||
| - | :<math>\frac{1}{1-x}=1+x+x^2+x^3+\cdots | + | :<math>(1+x)^n = 1 + n x + \frac{n(n-1)}{2}x^2+\frac{n(n-1)(n-2)}{3!}x^3+ \cdots</math> |
| + | |||
| + | :<math>\frac{1}{1-x}=1+x+x^2+x^3+\cdots </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>\frac{1}{(1-x)^2}=1+2x+3x^2+4x^3+\cdots </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>-\ln(1-x)=x+\frac{x^2}{2}+\frac{x^3}{3}+\cdots </math> | ||
| - | :<math>\ | + | :<math>\mathrm{e}^x=1+x+\frac{x^2}{2}+\frac{x^3}{3!}+\cdots </math> |
| - | :<math> | + | :<math>cos(x)=1-\frac{x^2}{2}+\frac{x^4}{4!}+\cdots </math> |
| - | :<math>\mathrm{ | + | :<math>\mathrm{sen}(x)=x-\frac{x^3}{6}+\frac{x^5}{5!}+\cdots </math> |
| - | :<math> | + | :<math>\mathrm{arctg}(x)=x-\frac{x^3}{3}+\frac{x^5}{5}+\cdots </math> |
| - | : | + | [[Categoría:Herramientas matemáticas (GIE)]] |
última version al 16:31 11 oct 2011
Contenido |
1 Reglas de derivación
- Suma de funciones
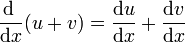
- Producto de funciones
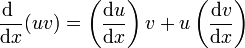
Caso particular u = C = cte
- Regla de la cadena
Caso particular de derivada logarítmica
Caso particular de exponencial de una función
2 Tabla de derivadas
| f(x) | df / dx | f(x) | df / dx |
|---|---|---|---|
| 
| 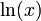
| 
|
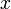
| 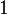
| 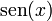
| 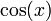
|
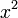
| 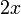
| 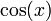
| 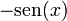
|

| 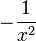
| 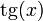
| 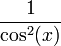
|
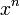
| 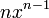
| 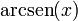
| 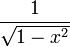
|
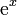
| 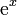
| 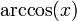
| 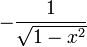
|
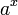
| 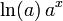
| 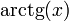
| 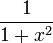
|
3 Tabla de primitivas
| f(x) | 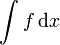
| f(x) | 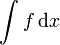
|
|---|---|---|---|
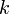
| 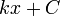
| 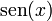
| 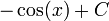
|
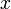
| 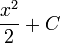
| 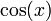
| 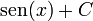
|

| 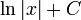
| 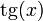
| 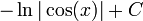
|
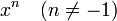
| 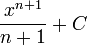
| 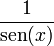
| 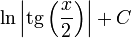
|
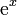
| 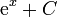
| 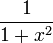
| 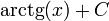
|
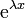
| 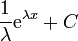
| 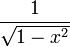
| 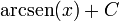
|
Más primitivas en la Wikipedia